Harnessing Fusion Energy: The Path to Limitless Power
11 December 2025
Let’s face it—we’re power-hungry creatures. From charging our phones to powering massive cities, we crave energy like coffee on a Monday morning. And while we’ve come a long way with renewables like solar and wind, there’s something even more powerful on the horizon: fusion energy.
It sounds like science fiction, doesn't it? A futuristic dream where we tap into the very reaction that powers the stars. But guess what? We’re slowly but surely figuring it out. And if we crack the code, fusion energy could change everything.
So buckle up. We’re diving deep into the world of fusion, why it’s the holy grail of clean power, the challenges holding it back—and how we just might be standing on the edge of a true energy revolution.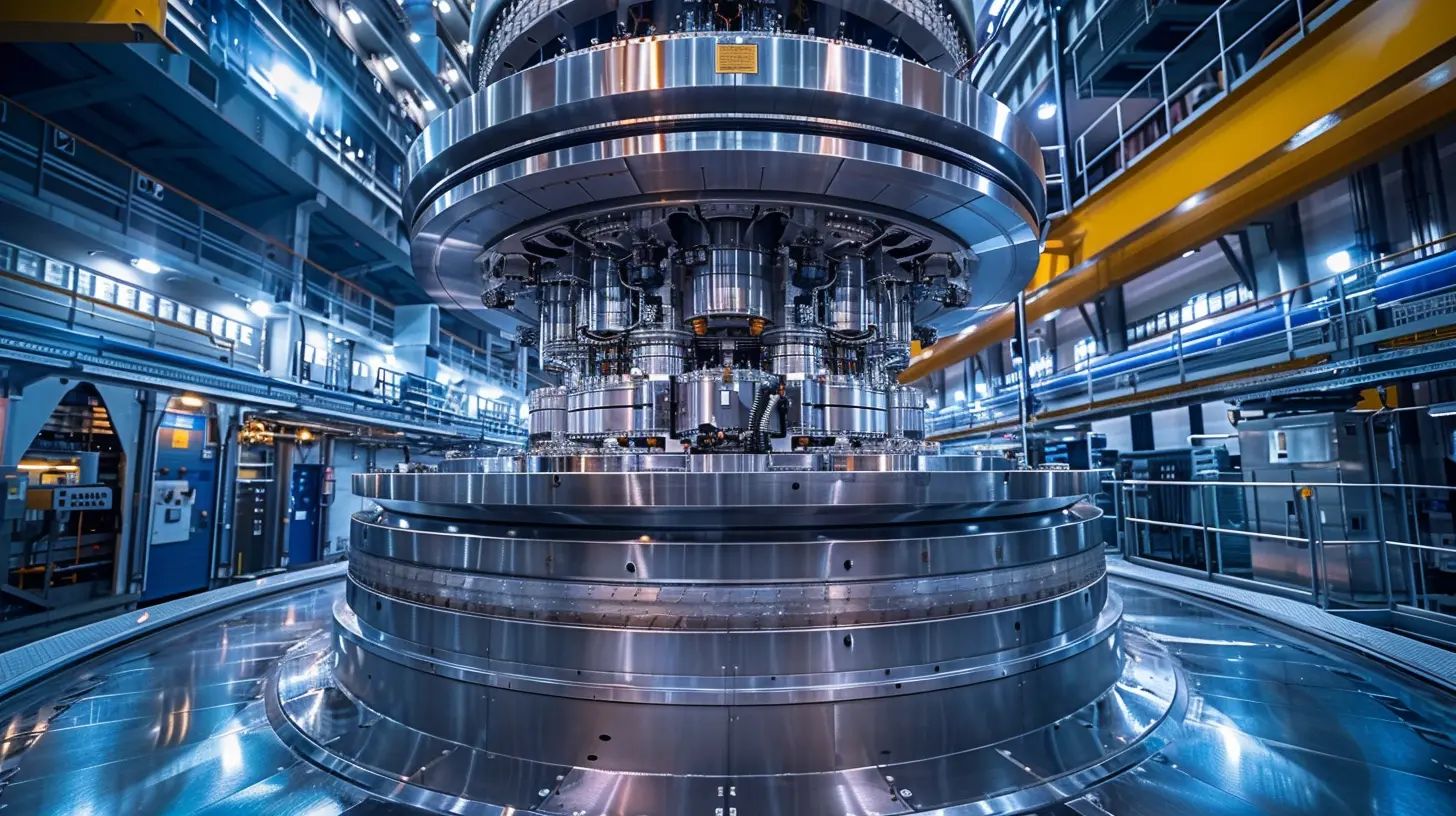
What Is Fusion Energy (And Why Should You Care?)
Let’s break it down.Fusion is the process where two light atomic nuclei smash together to form a heavier nucleus. In that moment, a mind-blowing amount of energy gets released. It’s the same reaction that makes the sun shine. Seriously—every second, the sun fuses over 600 million tons of hydrogen into helium. That’s a LOT of firepower.
Now imagine harnessing that same reaction here on Earth. One small cup of fusion fuel could potentially produce as much energy as burning over 1,000 tons of coal. No carbon emissions, no radioactive waste nightmares. Just clean, virtually unlimited energy.
Sounds amazing, right? But there’s a catch...
Fusion vs. Fission: Know the Difference
You’ve probably heard of nuclear power, but here’s a fun fact: what we currently use is fission, not fusion. Fission splits atoms apart, usually uranium or plutonium, and releases energy—but it also produces radioactive waste and can be risky (hello, Chernobyl and Fukushima).Fusion, on the other hand, smashes atoms together. It's much cleaner and way safer. There’s no meltdown risk because if something goes wrong in a fusion reactor, the reaction just fizzles out.
Here’s a quick analogy: fission is like breaking a plate into pieces (messy and dangerous), while fusion is like gluing two pieces of clay together until they become something new (cleaner and more stable).
Why Fusion Energy Is the Ultimate Prize
Let’s get real. The benefits of fusion go way beyond just powering your TV.1. Limitless Fuel Supply
Fusion uses hydrogen isotopes, like deuterium and tritium. Deuterium can be extracted from seawater, and tritium can be bred from lithium. There’s enough fuel in the oceans to keep us going for millions of years. Yup—millions.2. No Carbon Emissions
Fusion doesn’t release CO₂ or methane. In the age of climate change, that’s a game-changer. It's like having a supercar that runs on water and never pollutes.3. Minimal Waste
Fusion produces very little radioactive material—and what it does produce is way less dangerous and decays quickly. It's the nuclear option without the nuclear baggage.4. Safe by Design
Fusion reactions require extreme temperatures and pressure. If anything goes wrong, the reaction stops. Period. No chain reaction, no mushroom clouds.5. High Energy Output
Fusion has a massively high energy density. Just one gram of fusion fuel can produce as much energy as 10 tons of coal. That’s power efficiency on steroids.
The Science Behind Fusion: How Does It Work?
Alright, time to geek out a bit (don’t worry, I’ll keep it simple).Fusion needs three key ingredients:
1. Extremely high temperatures – We’re talking about 100 million degrees Celsius. Hotter than the sun’s core.
2. High pressure – To force atoms close enough for their nuclei to combine.
3. Containment – So the reaction doesn’t escape. Think of it like trying to bottle a star.
To make fusion happen, scientists use hydrogen isotopes—usually deuterium and tritium. When these collide at high speed, they fuse and release a neutron and a ton of energy.
But containing something that’s hotter than the sun? Yeah, that’s not exactly easy...
Tokamaks and Lasers: Ways We’re Trying to Bottle a Star
There are two main ways we’re attempting to harness fusion on Earth. And they sound straight out of a sci-fi movie.1. Magnetic Confinement (Tokamaks)
Tokamaks are donut-shaped devices that use powerful magnetic fields to trap super-hot plasma (that’s the fusion fuel) and keep it from touching the walls. The most famous tokamak is ITER, a huge international project in France. It’s the largest fusion experiment of its kind, and it aims to produce more energy than it consumes. Big deal? Absolutely.2. Inertial Confinement (Lasers, Baby!)
Here, scientists use super-powerful lasers to blast tiny fuel pellets, compressing them until fusion happens. The National Ignition Facility (NIF) in California made headlines by achieving a net energy gain in late 2022. That was a historic milestone. Think of it as lighting a firecracker with a magnifying glass—but way more intense.Challenges on the Fusion Frontier
OK, now you’re probably thinking: “If fusion is so great, why don’t we have it already?”Fair question. And the answer is: It’s HARD. Like, really hard.
1. Temperature Trouble
You need insanely high heat to start fusion. Creating and maintaining those temperatures without melting everything around is... a bit tricky.2. Plasma Control
Plasma is wild and unpredictable. It tends to escape its magnetic prison like a rebellious teenager. Keeping it stable is like trying to hold jelly with rubber bands.3. Energy Input vs. Output
For a long time, we had to put in more energy than we got out. Not exactly a winning formula. But recently, labs like NIF are changing the game.4. Material Limitations
No known material can withstand the conditions inside a fusion reactor for long. We’re developing new heat-resistant materials, but it's still a work in progress.5. Tritium Supply
Tritium isn't naturally abundant and is radioactive. We can breed it using lithium, but setting up the right infrastructure takes time.6. Cost and Time
Building fusion reactors is mind-blowingly expensive. ITER alone is a $20+ billion project and won’t be fully operational until the late 2030s. Fusion is a long game—but one worth playing.Fusion Energy Milestones: How Far Have We Come?
You might be surprised at how far we’ve actually come. Here are a few key milestones:- 1950s: First serious fusion research begins.
- 1983: JET (Joint European Torus) achieves a record energy output.
- 2010s: ITER construction ramps up.
- 2022: NIF hits ignition—more energy out than in.
These milestones aren’t just scientific wins—they’re stepping stones toward making fusion a real part of our energy mix.
Private Companies Are Getting in on the Action
It’s not just governments and massive labs anymore. The private sector is jumping in, and things are heating up (pun intended).Some Notable Players:
- Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) – Spin-off from MIT, using high-temperature superconducting magnets.- Helion Energy – Promising “fusion in five years” with a unique approach.
- TAE Technologies – Using beam-driven plasma physics to chase compact fusion reactors.
Investment in fusion startups hit over $2 billion in the last few years. Why? Because where there's competition, there's progress—and possibly profit.
When Could Fusion Energy Be a Reality?
Ah, the million-dollar question.The joke used to be: fusion is always 30 years away. But now? We’re closing in fast. Some hopefuls believe we’ll see commercial fusion reactors by the 2030s or early 2040s.
Sure, it won’t replace all our power plants overnight. But step by step, fusion could become a key piece of the clean energy puzzle. Combined with solar, wind, and storage, we might actually have a shot at a truly sustainable future.
What a Fusion-Powered World Could Look Like
Imagine cities glowing with clean energy. Industries powered without pumping CO₂ into the air. Cars and homes charged with electricity from a process cleaner than a mountain spring.- No blackouts when the sun doesn’t shine or the wind doesn’t blow.
- No oil wars or geopolitics over gas pipelines.
- No smoke stacks or nuclear waste to deal with.
Just pure, star-born energy lighting up the world.
Final Thoughts: The Bright Future of Fusion
Fusion energy isn’t a pipe dream—it’s a work in progress. And yeah, there’s a long road ahead. But the destination? Totally worth it.If we get this right, we’re talking about a world where energy is abundant, clean, and available to everyone. It’s not just about powering gadgets or keeping air conditioners running. It’s about lifting billions out of energy poverty, fighting climate change, and giving our planet a breather.
So the next time you hear about “harnessing the power of the stars,” don’t roll your eyes. Fusion might be the spark that powers our future—and maybe even saves it.
all images in this post were generated using AI tools
Category:
Future TechAuthor:

John Peterson
Discussion
rate this article
2 comments
Otto Diaz
Fusion energy isn't just a dream; it's our future. The potential for limitless, clean power is within our grasp, yet we must prioritize investment and innovation. Let’s shatter the barriers of doubt and embrace this revolutionary technology. The time to act is now—no more excuses.
January 14, 2026 at 4:21 AM

John Peterson
Absolutely! Fusion energy holds immense promise for a sustainable future. Prioritizing investment and innovation is crucial to overcoming the challenges ahead. Let’s seize this opportunity together!
Morgan Ortiz
Exciting advancements! Fusion energy could truly reshape our future for limitless power!
December 15, 2025 at 5:25 AM

John Peterson
Thank you! We're optimistic that fusion energy will pave the way for a sustainable and abundant energy future.


